Passwords are broken. They’re weak, reused, and easily compromised. Regular authentication methods can’t keep up with evolving fraud tactics in a digital economy that moves billions in seconds.
This has pushed financial institutions to adopt biometrics as a faster, more secure alternative. From mobile banking logins to verifying new customers, face recognition is now embedded in the daily workflow of many banks, fintechs, and payment platforms.
According to Juniper Research, the number of digital ID verification checks is expected to reach 86 billion in 2025, up from 75 billion in 2024. In banking alone, nearly 83% of global financial institutions are exploring or already using some form of biometric verification.
On the surface, biometrics seem like a win. They reduce fraud, speed up onboarding, and eliminate the need for passwords. But beneath the convenience lies a growing regulatory and ethical minefield.
Laws like the EU’s GDPR and Illinois’ BIPA impose strict conditions on collecting, storing, and using biometric data. A single misstep can lead to multi-million-dollar fines. Meanwhile, concerns over data privacy, algorithmic bias, and lack of transparency fuel public backlash.
Biometrics in finance may be the future, but how they’re implemented will determine whether they’re a breakthrough or a compliance nightmare.
This blog explores the evolving role of biometrics in financial services, examining how technologies like facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice authentication are transforming security protocols, enhancing customer experiences, and addressing regulatory compliance.
How Biometrics in Financial Services Work: Key Stages and Processes
Biometrics in financial services refers to using an individual’s unique physical or behavioral traits to verify identity. These traits help institutions secure transactions, control access, and streamline authentication processes without relying on passwords or PINs. Biometrics ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive financial systems or perform specific operations. The implementation involves several key stages:
1. Enrollment
During enrollment, specialized sensors or devices capture a customer’s biometric data, such as a fingerprint, facial image, or voice sample. This data is then converted into a digital template through feature extraction algorithms.
The resulting template, not the raw biometric data, is securely stored in the bank’s database or the customer’s device, ensuring privacy and security.
2. Storage
The biometric templates are stored in encrypted form to prevent unauthorized access. Banks may store this data centrally or locally on the customer’s device, depending on the security architecture and regulatory requirements.
Local storage, such as on a secure element within a smartphone, can enhance privacy by keeping biometric data under the user’s control.
3. Verification
When authentication is required, such as during login or transaction approval, the system captures a new biometric sample from the customer. This sample is processed and compared to the stored template using matching algorithms. The customer’s identity is verified if the new sample matches the stored template within an acceptable threshold.
4. Integration with Banking Services
Biometric authentication is integrated into various banking services:
- Mobile Banking Apps: Customers can log in using fingerprint or facial recognition, eliminating the need for passwords.
- ATMs: Some ATMs are equipped with biometric scanners, allowing cardless transactions through fingerprint or palm vein recognition.
- Customer Service: Voice recognition can authenticate customers during phone interactions, streamlining service delivery.
Types of Biometric Technologies Used in Financial Services
Below are the primary types of biometric technologies used in financial services:
1. Facial Recognition
Facial recognition identifies and verifies individuals by analyzing their facial features. It uses either 2D or 3D mapping to capture the shape and contours of a person’s face. 2D mapping captures flat images, while 3D mapping collects depth data for improved accuracy and resistance to spoofing attempts (e.g., photos or videos).
Liveness detection ensures the input is from a live person, not a static image or recording. Techniques include blinking detection, head movement, and thermal sensing. Facial recognition is commonly integrated into mobile banking apps and digital kiosks for login and identity verification.
2. Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint recognition matches the ridges and patterns of a user’s fingerprint against stored templates. Fingerprint biometrics in financial services are widely used for unlocking banking apps and ATM authentication.
This type of technology includes speed, low cost, and ease of use. However, it requires physical contact, which can be less hygienic and less effective if fingers are wet or damaged. Facial recognition is more convenient in contactless environments.
3. Iris and Retina Scanning
These technologies analyze patterns in the colored ring around the pupil (iris) or the blood vessels at the back of the eye (retina). Iris and retina scans offer extremely high accuracy but require specialized cameras and proximity. This limits their widespread use in consumer-facing financial applications.
4. Voice Recognition
Voice biometrics identify individuals by analyzing vocal characteristics such as pitch, tone, and speaking style. Many banks use voice recognition during customer service calls. Users can verify their identity by speaking a specific phrase or during a natural conversation.
5. Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics in financial services involve analyzing subtle user interactions such as typing patterns, mouse movements, screen pressure, and navigation habits. These behaviors are unique to each individual and are difficult for fraudsters to replicate.
As a result, they serve as an additional layer of security that operates silently in the background. Financial institutions use these behavioral indicators to monitor user sessions in real time. When deviations from established behavior patterns are detected, the system can flag potential threats such as account takeover attempts or automated fraud, allowing for proactive risk management and response.
Why Are Biometrics Essential for Modern Banking Operations?
As digital banking becomes the norm, conventional security methods are insufficient to protect users and financial institutions from evolving threats. Below are the core reasons why banks are increasingly adopting biometric technologies:
1. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Banks are required by law to verify the identities of their customers, particularly during onboarding and transactions. Regulations like the Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) frameworks mandate strong identity verification processes. Additionally, Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) in the European Union requires strong customer authentication (SCA), which can be fulfilled through biometric verification.
Biometric technologies, such as facial recognition, fingerprint scans, or voice authentication, provide reliable, tamper-resistant identity verification. By using these methods, banks reduce the risk of regulatory penalties while maintaining customer trust.
2. Fraud Prevention
Fraudulent activities such as identity theft and account takeovers are a growing concern. According to the Javelin Strategy & Research 2024 Identity Fraud Study, account takeover fraud resulted in $15.6 billion in losses in 2024, up from $12.7 billion in 2023.
Biometric authentication makes it significantly harder for unauthorized users to gain access, as biometric traits cannot be easily duplicated or shared. Many banks now use multi-factor authentication (MFA) by combining biometrics with passwords or PINs. This layer ensures that access requires both something the user knows and something the user is, significantly reducing fraud risk.
3. Improved Customer Convenience
User experience is a key differentiator in the financial sector. Biometric authentication allows for faster logins and transactions, reducing friction for customers. It eliminates the need for passwords, which are often forgotten or reused, and enables real-time identity verification during onboarding and service requests.
This speed and simplicity improve customer satisfaction and reduce abandonment rates during digital sign-up processes. According to Juniper Research, biometric authentication is projected to secure over $2.5 trillion worth of mobile payment transactions by 2024, marking a significant increase from previous years. This reflects the growing customer preference for seamless, secure access to banking services.
Practical Applications of Biometrics in the Financial Sector
Biometric technologies have become integral to modern banking, enhancing security, streamlining operations, and improving customer experiences. Below are applications of biometrics in the financial sector, each supported by real-world implementations.
1. Customer Onboarding & KYC
Banks utilize biometric systems to verify customer identities during account opening processes. Institutions can authenticate users remotely by comparing live facial scans with official identification documents, reducing the need for physical branch visits.
Advanced biometric solutions enable real-time verification through selfies and ID scans, expediting the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. This accelerates onboarding and minimizes the risk of identity fraud.
Moody’s Analytics highlights the increasing adoption of biometrics in KYC compliance, noting that biometric data offers both security and reliability, unlike physical documents, which might be faked or harder to review in a digital process.
2. Transaction Authentication
For high-value transactions, biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, adds an extra layer of security. Only authorized individuals can approve significant transfers or changes to their accounts. Biometrics are increasingly replacing PINs and passwords in mobile banking, offering a more secure and user-friendly authentication method.
3. Access Control in Banks & ATMs
Banks are implementing facial recognition systems within branches to control access to secure areas and enhance customer service by quickly identifying clients. ATMs equipped with biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, allow customers to perform transactions without physical cards, reducing the risk of card-related fraud.
OCBC Bank in Singapore has rolled out facial verification for ATM banking, enabling customers to withdraw cash using facial recognition technology.
4. Fraud Detection & Risk Management
Biometric systems analyze user behavior patterns to identify unusual activities that may indicate fraudulent attempts, such as deviations in typing speed or navigation habits. Combining biometrics with artificial intelligence enhances the detection of synthetic identities and fraudulent behaviors, allowing for proactive risk management.
5. Payments and Wallet Authentication
Mobile payment platforms like Apple Pay and Google Pay utilize biometric authentication, such as Face ID or fingerprint recognition, to authorize transactions, enhancing security and user convenience. Biometric authentication streamlines the payment process, allowing users to complete transactions quickly without passwords or physical cards.
Amazon has introduced palm recognition technology, enabling customers to pay at Whole Foods Market stores by scanning their palm and linking biometric data to payment information for a seamless checkout experience.
Face Recognition & Biometrics in Finance: A Strategic Advantage or a Governance Challenge
Biometric technologies, including facial recognition, are increasingly integral to modern banking, offering enhanced security and streamlined user experiences. However, their adoption introduces specific challenges that financial institutions must address.
1. Security Risks in Biometric Systems
While biometrics provide robust authentication, they are not impervious to security threats:
- Data Breaches: Unlike passwords, biometric data is immutable. If compromised, it cannot be changed, posing long-term security concerns.
- Spoofing Attacks: Techniques such as using high-resolution images or synthetic artifacts can deceive biometric systems, granting unauthorized access.
- Centralized Storage Vulnerabilities: Storing biometric data in centralized databases can make it a lucrative target for cyberattacks.
Implementing measures like liveness detection and decentralized storage can mitigate these risks.
2. Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The use of biometric data in banking is subject to stringent regulations:
- Data Protection Laws: Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) classify biometric data as sensitive, requiring explicit user consent and robust protection measures.
- International Variability: Compliance requirements differ across jurisdictions, complicating global implementation strategies.
Financial institutions must ensure transparency in data usage and establish clear consent protocols to navigate these regulatory landscapes.
3. Ethical and Privacy Considerations
The deployment of biometric systems raises ethical questions:
- User Consent: Ensuring informed and voluntary participation is crucial.
- Data Usage Transparency: Users should know how their biometric data is collected, stored, and utilized.
- Potential for Misuse: Biometric data could be used beyond its intended purpose, leading to privacy infringements.
Addressing these concerns requires clear policies and user education.
4. Technological Limitations and Bias
Biometric systems can exhibit performance disparities. Factors like lighting conditions and facial changes can affect recognition accuracy. Studies have shown that some biometric systems have higher error rates for specific demographic groups, leading to potential discrimination. Continuous system training with diverse datasets is essential to enhance accuracy and fairness.
5. Operational and Cost Implications
Implementing biometric systems involves a significant investment. Acquiring and maintaining biometric hardware and software can be expensive. Ensuring compatibility with existing banking systems requires careful planning and resources. The long-term security and user convenience benefits can justify the investment despite these costs.
Avahi AI’s Facial Recognition: Streamlining Identity Verification in Finance
Avahi AI platform offers a facial recognition feature to enhance identity verification processes within the financial sector. This tool allows institutions to authenticate users efficiently and securely.
How It Works
1. Image Upload: Users upload a clear image of their face through the platform’s interface.
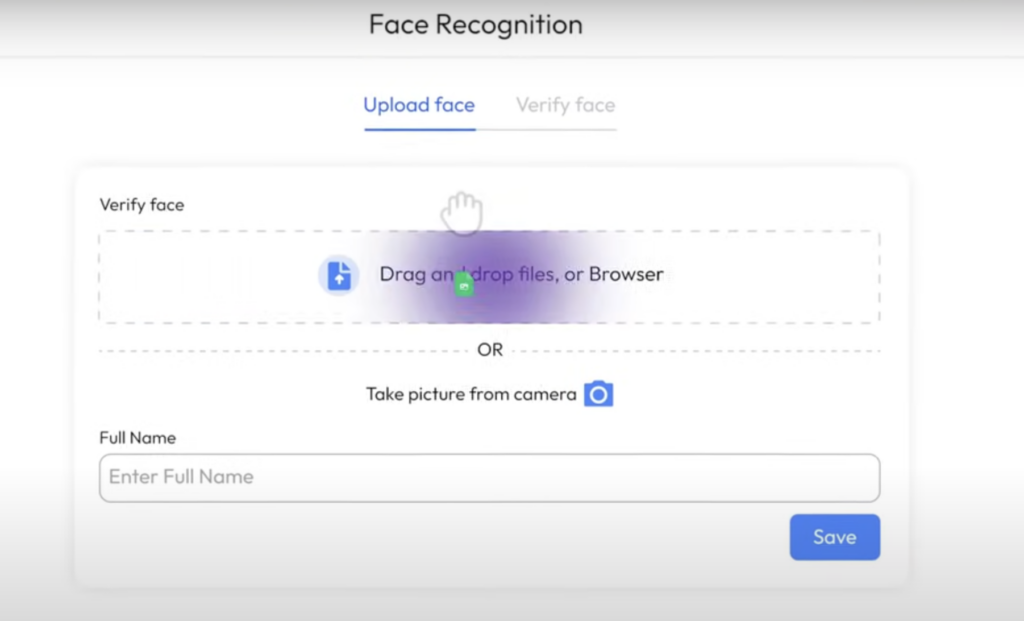
2. Facial Analysis: The system analyzes unique facial features using advanced algorithms.
4. Identity Matching: The analyzed data is compared against official records or documents to verify the user’s identity.
4. Result Delivery: The system provides a verification result, confirming whether the identity matches the provided information
Benefits of Avahi AI’s Facial Recognition for the Financial Sector
Avahi AI’s facial recognition technology offers a suite of advantages tailored to the needs of financial institutions. Using advanced biometric solutions, banks and financial services can enhance security, streamline operations, and improve customer experiences. Below is an in-depth look at the key benefits:
1. Enhanced Security
Facial recognition provides a robust layer of security by utilizing unique facial features that are difficult to replicate. This biometric authentication method mitigates risks associated with traditional security measures, such as passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten, stolen, or hacked.
By implementing facial recognition, financial institutions can ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive financial information or perform transactions and deter fraudulent activities by making it challenging for imposters to mimic biometric traits.
This also helps to add an extra layer of verification for high-value or sensitive transactions, ensuring legitimacy.
2. Efficient Customer Onboarding
Conventional customer onboarding processes can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Avahi AI’s facial recognition streamlines this as customers can verify their identities in real time by simply uploading a selfie matched against official identification documents.
This eliminates the need for in-person visits, allowing customers to open accounts or access services from anywhere. Automating the verification process decreases the reliance on manual checks, leading to cost savings.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with regulations such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is critical in the financial sector. Facial recognition technology is pivotal in meeting these compliance requirements by providing accurate identity verification. Financial institutions can significantly reduce the risk of identity fraud by ensuring that customers are who they claim to be.
Moreover, facial recognition systems facilitate the maintenance of detailed records of verification processes, which are essential for audits and compliance reporting. Integrating facial recognition with real-time monitoring systems allows for continuous observation of transactions and user behavior, aiding in the early detection of suspicious activities and enhancing overall risk management.
4. Improved User Convenience
User experience is paramount in retaining customers. Users can access their accounts or authorize transactions with a quick facial scan. This eliminates the need to remember complex passwords and reduces the time to complete transactions, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Facial recognition allows for touchless authentication, which is especially relevant in the current health-conscious environment.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness AI’s full potential while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Utilize Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to enhance automation and decision-making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, fraud detection, and secure model deployment.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Get Started with Avahi’s AI Platform!
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why are banks adopting biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication reduces fraud, speeds up onboarding, and eliminates the need for passwords. It also helps banks comply with regulations like KYC, AML, and PSD2 that require strong customer identity verification.
- Is biometric data more secure than traditional passwords?
Yes. Biometrics are harder to replicate or steal compared to passwords. However, secure storage and encryption are critical because biometric data can’t be changed once compromised.
- What compliance risks are associated with using biometrics?
Biometric data is considered sensitive under laws like GDPR and BIPA. To avoid legal and financial penalties, financial institutions must obtain explicit user consent, ensure data protection, and maintain transparency.
- Can biometric systems be spoofed or hacked?
Yes, through methods like high-resolution photos or deepfakes. However, advanced systems use liveness detection and behavioral monitoring to counter spoofing attempts.
- How does biometric technology improve customer onboarding?
Facial recognition and other biometrics allow users to verify their identity remotely, reducing the need for branch visits. This speeds up the KYC process, improves accuracy, and enhances the user experience.




